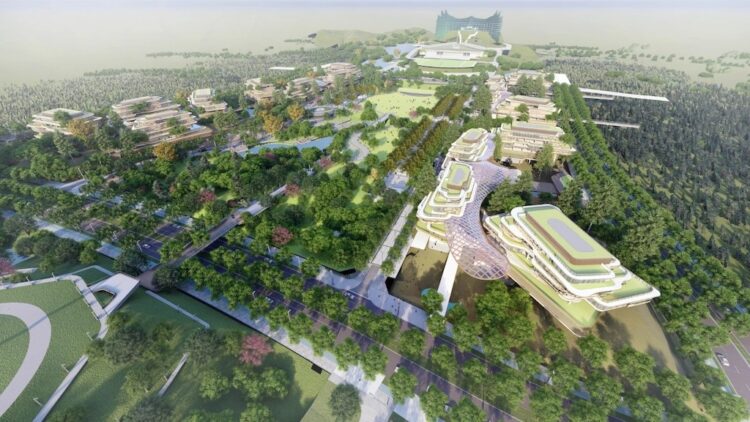
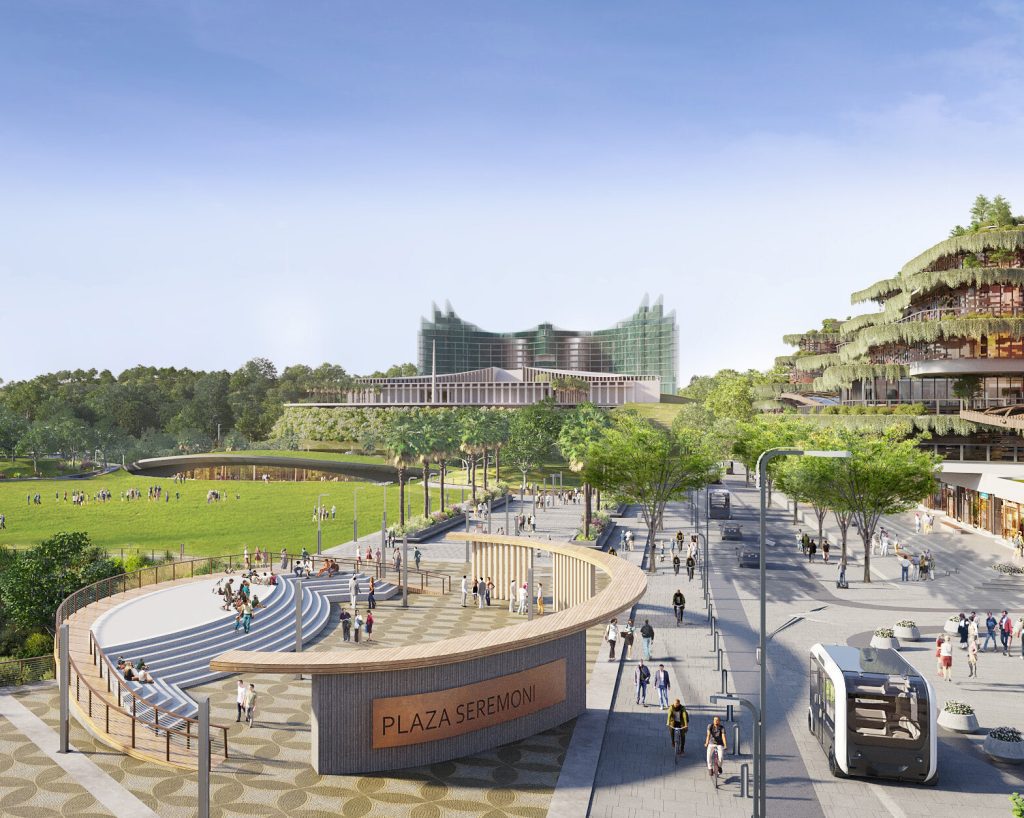
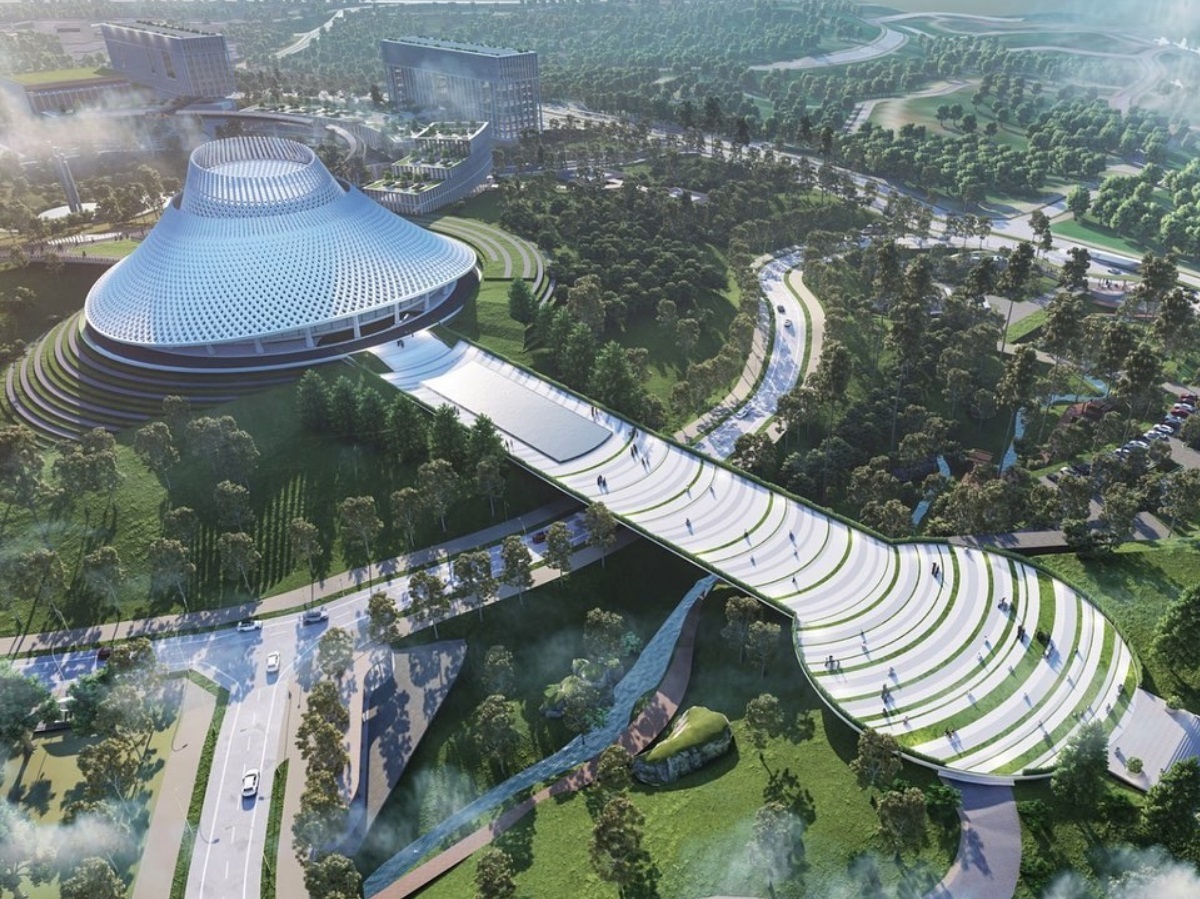
indonesia is embarking on an ambitious journey to relocate its capital from Jakarta to a newly planned city named Nusantara. This initiative is driven by the pressing challenges Jakarta faces, including severe congestion, pollution, and the alarming rate at which the city is sinking. Nusantara is envisioned as a smart, sustainable, and inclusive city that integrates advanced technology with environmental consciousness. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of Nusantara’s development, highlighting its objectives, technological innovations, environmental strategies, and the challenges it aims to overcome.
The Rationale Behind Relocating the Capital
A. Environmental and Urban Challenges in Jakarta
Jakarta, home to over 10 million residents, is grappling with significant environmental issues. The city is sinking at an alarming rate of up to 20 centimeters annually, primarily due to excessive groundwater extraction and rising sea levels. Projections indicate that parts of North Jakarta could be submerged by 2050 .
B. Strategic Vision for National Development
The decision to establish Nusantara aligns with Indonesia’s broader vision for equitable national development. By relocating the capital to East Kalimantan, the government aims to distribute economic growth more evenly across the archipelago, reducing the concentration of development in Java and fostering new economic hubs .
Nusantara: A Blueprint for a Smart and Sustainable City
A. Human-Centered Urban Design
Nusantara’s urban planning emphasizes a human-centered approach, focusing on enhancing the quality of life for its residents. The city is designed to be walkable, with integrated public transportation systems, green spaces, and community-centric amenities .
B. Integration of Advanced Technologies
The city will leverage cutting-edge technologies to optimize urban management and services:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT): Deployed for real-time monitoring of traffic, air quality, and public safety.
-
Smart Grid Systems: To manage energy distribution efficiently, incorporating renewable energy sources like solar power.
-
Autonomous Public Transportation: Including hydrogen-powered vehicles and autonomous trams to reduce carbon emissions .
C. Digital Governance and Citizen Engagement
Nusantara aims to implement a digital governance model that facilitates transparent and efficient public services. The IKNOW application serves as a centralized platform for residents to access information, report issues, and engage with government services .
Environmental Sustainability Initiatives
A. Commitment to Carbon Neutrality
The city is designed with a strong emphasis on environmental sustainability:
-
Renewable Energy Utilization: Aiming for 100% renewable energy usage by 2045, primarily through solar power and other sustainable sources.
-
Green Building Standards: Implementing energy-efficient designs and materials to minimize environmental impact .
B. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Preservation
Given its location in a biodiverse region, Nusantara’s development includes measures to protect local ecosystems:
-
Conservation of Natural Habitats: Efforts to preserve the surrounding forests and wildlife, including species like the Kalimantan orangutan.
-
Integration of Green Spaces: Incorporating parks and natural areas within the urban landscape to maintain ecological balance .
Economic and Social Considerations
A. Investment and Funding Strategies
The estimated cost for developing Nusantara as a smart city ranges between $18.7 billion and $25 billion. While the government has allocated initial funding, attracting private and foreign investment is crucial for the project’s success .
B. Empowerment of Local Communities and MSMEs
The development plan includes initiatives to support micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs):
-
Digital Platforms: Providing tools for MSMEs to engage in e-commerce, manage logistics, and access market information.
-
Training and Incentives: Offering programs to enhance digital literacy and business skills among local entrepreneurs .
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
A. Ensuring Inclusive Development
A critical challenge is to ensure that the benefits of Nusantara’s development are equitably distributed:
-
Community Engagement: Involving local and indigenous communities in the planning and decision-making processes.
-
Addressing Digital Divide: Implementing educational programs to improve digital literacy across all demographics .
B. Environmental and Social Impact Management
Balancing development with environmental preservation requires careful planning:
-
Sustainable Construction Practices: Utilizing eco-friendly materials and minimizing deforestation.
-
Monitoring and Evaluation: Establishing systems to assess the environmental and social impacts continuously and adjust strategies accordingly .
Conclusion
Nusantara represents a bold vision for Indonesia’s future—a smart, sustainable, and inclusive capital that addresses the challenges of modern urbanization. By integrating advanced technologies with a commitment to environmental stewardship and social equity, Nusantara aims to set a precedent for future urban developments globally. The success of this endeavor will depend on effective implementation, continuous community engagement, and the ability to adapt to emerging challenges